EGFR mutation, as one of the most common driving genes in NSCLC, has an incidence rate of approximately 50% in lung adenocarcinoma patients in China [1]. In recent years, EGFR-TKI has brought good survival prognosis to EGFR mutation positive patients, but there are still some patients who are not sensitive to EGFR-TKI treatment in clinical practice.
With the deepening understanding of lung cancer, the association between different driver gene mutations and the efficacy of EGFR-TKI has been discovered. Patients with EGFR Ex20ins NSCLC are generally insensitive to first, second, and third-generation EGFR-TKI therapy, and there are currently no good first-line treatment targeted drugs available.
The 2023 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting was held grandly from June 2 to June 6 in Chicago, USA. Professor Duan Jianchun from the Cancer Hospital of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, representing Professor Wang Jie's study team, taking the study data of the third generation EGFR-TKI——YK-029A presented the study data "Safety and preliminary efficacy of YK-029A, a new EGFR TKI, in patients with advanced NSCLC hardware Ex20ins, T790M or rare mutations" (Abstract No. 9014) at the meeting [2], this drug has been recognized as a breakthrough therapy for EGFR Ex20ins NSCLC initial treatment. EChinaHealth combined with "DXY Tumor Time" invited Professor Duan Jianchun to give a wonderful interpretation of the diagnosis and treatment status and new breakthroughs of EGFR Ex20ins NSCLC.

The dilemma of first-line treatment for EGFR non sensitive mutations urgently needs to be overcome
EGFR-TKI is the first-line standard treatment for EGFR mutation positive NSCLC, but for some mutation subtypes, EGFR-TKI has poor efficacy, and EGFR Ex20ins NSCLC is one of them. The main reason is the unique spatial structure of EGFR Ex20ins, making it difficult for EGFR TKI to bind to ATP binding pockets; The activation state of Ex20ins mutation is highly similar to that of wild-type EGFR. Increasing the activity of Ex20ins will also simultaneously increase the inhibition of wild-type EGFR, and selectivity cannot be balanced; There are multiple types of mutations and strong heterogeneity at the same time. Currently, domestic and foreign guidelines for first-line treatment of EGFR Ex20ins NSCLC refer to driver gene negative NSCLC, and there is no effective targeted treatment method yet.
Professor Duan Jianchun stated that, “there are many mutation sites in the NSCLC EGFR Ex20ins, and there are currently over 100 known EGFR Ex20ins sites. In addition, the spatial conformation of EGFR Ex20ins is similar to that of EGFR wild-type. Traditional EGFR-TKI requires a higher dose to achieve effective drug concentration, which may lead to intolerable adverse reactions.”
“YK-029A is a third-generation EGFR-TKI with improved drug structure. It not only has good anti-tumor effects on EGFR sensitive mutation NSCLC, but also effectively inhibits non sensitive mutation types. In both cell line and animal trial models, YK-029A showed good sensitivity to EGFR Ex20ins. Therefore, the required dosage to achieve therapeutic effects is lower than traditional EGFR-TKI, implying better therapeutic effects.”
Phase I clinical study results announced, surprising efficacy of YK-029A
The Phase I clinical study announced at this ASCO Meeting explored the efficacy of YK-029A in the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC patients with EGFR Ex20ins mutations, as well as in treated EGFR T790M or rare NSCLC patients. Administer medication doses of 50, 100, 150, 200, and 250mg/day respectively. The main study objectives are safety assessment, as well as exploring dose limited toxicity (DLT) and maximum tolerable dose (MTD). In the untreated EGFR Ex20ins mutant NSCLC cohort, patients received YK-029A 200mg/d, 28 days/cycle of treatment.
A total of 108 patients were included in the safety analysis, and the results showed that:
DLT did not occur during the dose escalation Phase, and MTD did not reach;
The incidence of adverse events (TEAEs) during treatment was 98.1%, of which 38% were ≥ grade 3 TEAEs;
The incidence of treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) was 94.4%, of which 27.8% were ≥ grade 3 TRAEs.
One patient died of liver abscess related to YK-029A, and three patients terminated treatment due to TEAE. The most common types of TRAE are diarrhea (46.3%), anemia (38.0%), and rash (32.4%).
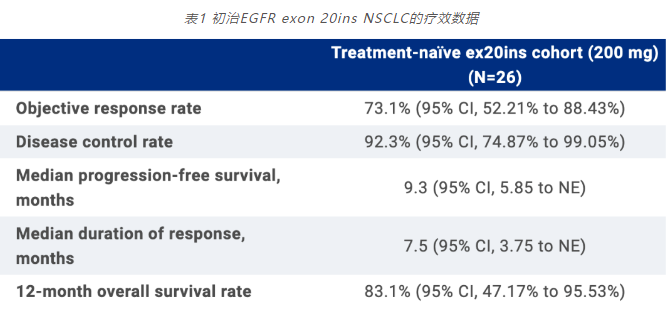
A therapeutic analysis was conducted on 26 newly treated patients with EGFR Ex20ins mutation lung cancer, of which 96.4% were lung adenocarcinoma and 85.7% were stage IV patients.
As of October 30, 2022, 73.1% of patients achieved partial remission (PR), 19.2% of patients achieved disease stability, and 7.7% of patients experienced disease progression. The confirmed objective response rate was 73.1% (95% CI 52.21% -99.43%), median progression free survival (PFS) was 9.3 months (95% CI 5.85 months NE), disease control rate (DCR) was 92.3% (95% CI 74.87% -99.05%), median disease control time (DOR) was 7.5 months (95% CI 3.75 months NE), and 12-month survival (OS) rate was 83.1% (95% CI 47.17% -95.53%).
In the Phase I study, Professor Wang Jie's team designed a 3+3 dose ramp up sequence. The results showed that at lower doses, YK-029A had good therapeutic effects on NSCLC with EGFR T790M, EGFR Ex20ins and other mutations. The ORR assessed by the independent review committee exceeded 70%, and the median PFS exceeded 9 months. In terms of safety, there were no unexpected adverse events, and the incidence of adverse events ≥ level 3 was relatively low, resulting in a lower incidence of AEs leading to drug discontinuation.
Professor Duan Jianchun said, "Based on the positive results of this study, we quickly conducted a Phase III clinical study on the first-line treatment of EGFR Ex20ins NSCLC with YK-029A". We look forward to the prompt results of this study, which will bring better treatment plans and more treatment options for EGFR Ex20ins patients.
YK-029A has been designated as a breakthrough therapy (BTD), bringing new choices for EGFR Ex20ins in the initial treatment of lung cancer
Professor Duan Jianchun stressed that lung cancer is the malignant tumor with the highest incidence rate and mortality in China, threatening the life and health of our people. Currently, there are still many unmet treatment needs.
In recent years, with the continuous improvement of R&D capabilities, many new drugs have emerged in China, including small molecule targeted drugs, immune checkpoint inhibitors, dual antibodies, and antibody drug conjugates (ADCs). These new drugs provide more suitable drugs for the Chinese population and greatly improve the accessibility of advanced therapies, playing an important role in the "Healthy China 2030" plan and enhancing people's sense of happiness in life.
In terms of EGFR Ex20ins treatment, with the approval of TAK-788, DZD9008 has been prioritized for approval, providing targeted treatment options for EGFR Ex20ins patients who have failed standard chemotherapy. For patients with initial diagnosis and treatment, chemotherapy or chemotherapy-based combination therapy is currently the preferred treatment method, but the overall efficacy is poor. YK-029A has been designated as a breakthrough therapy (BTD) by the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) in the field of initial treatment of EGFR Ex20ins in lung cancer, reflecting the recognition of YK-029A study quality by drug regulatory agencies and filling the gap in the first-line treatment of EGFR Ex20ins NSCLC lacking effective targeted drugs.
Professor Duan Jianchun said, "For NSCLC patients who are sensitive to targeted therapy, if they can be used on the front line, their treatment effectiveness is higher than their effectiveness on the back line, and patients will benefit more. The concept of "using good medicine first" has become widely recognized. Compared with traditional chemotherapy, small molecule targeted drugs have advantages in convenience and safety. If the accessibility of small molecule targeted drugs can be improved, good drugs can be used for lung cancer patients, and the "chronic disease" of lung cancer is no longer unattainable."
Rare target mutated tumors still need attention, innovative drugs are the only choice to overcome difficulties
In the past, due to the small number of cases of rare mutated tumors, it was difficult to enroll in clinical study, and the development of new drugs was also limited. Professor Duan Jianchun shared the clinical study process of NTRK inhibitors regarding this current situation.
NTRK fusion occurs in many solid tumors, but the overall incidence is low. Through basket trials, more patients with rare gene mutations can be recruited to explore their corresponding treatment plans. Currently, NTRK inhibitors have shown very good therapeutic effects in many types of cancer.
The exploration of treatment options for rare mutated tumors can refer to NTRK inhibitors for cross tumor clinical studies. If it can be effective and applied for breakthrough therapy certification, perhaps clinical popularization will soon be achieved in the future, benefiting more patients.
As a third-generation EGFR-TKI, YK-029A has a good inhibitory effect on many EGFR insensitive mutations. For non-sensitive mutations with a high incidence of EGFR mutations, EGFR Ex20ins NSCLC lacks good first-line targeted therapeutic drugs. The clinical study released by Professor Duan Jianchun shows that YK-029A has good tolerance and shows initial efficacy in locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC with EGFR 20ins mutation. In addition, YK-029A has good anti-tumor efficacy for mutations such as EGFR T790M.
With more and more clinical study data being released, YK-029A may become a promising first-line treatment option for EGFR Ex20ins NSCLC in the future. At present, YK-029A has been recognized as a breakthrough therapy for the treatment of EGFR Ex20ins NSCLC, and its Phase III clinical study is currently underway. We look forward to more and more innovative Chinese drugs going abroad, entering clinical trials as soon as possible, and benefiting more cancer patients.
References:
[1] Zeng Lei, Yang Kaixuan Progress in targeted therapy for advanced NSCLC [J] West China Medicine, 2021,36 (01): 102-109
[2] Safety and preliminary efficacy of YK-029A, a novel EGFR TKI, in patients with advanced NSCLC harboring ex20ins, T790M or rare mutations. 2023 ASCO,poster 9031