Beijing, China, September 28, 2025 - Suzhou Puhe BioPharma Co., Ltd. announced that PH027-1, a potential best-in-class WRN small-molecule inhibitor, has been approved for IND by the NMPA. Puhe has independently developed PH027-1 and owns full intellectual property rights to it. This makes it the first domestic WRN-targeting small-molecule compound to receive full clinical trial approval. PH027-1 is Puhe's fourth project to enter the clinical stage.
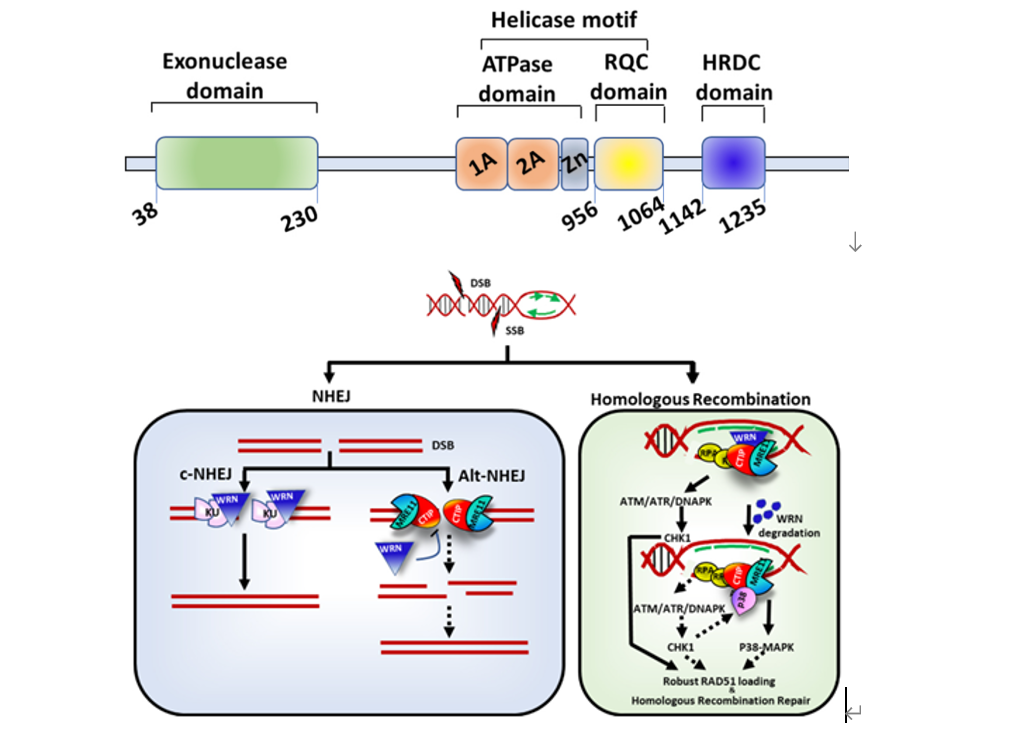
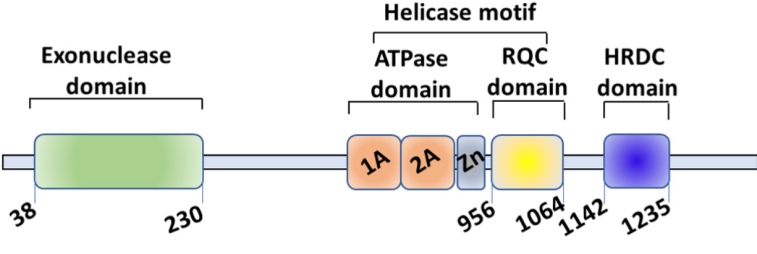
WRN is a member of the RecQ DNA helicase family and the only protein in this family with an exonuclease domain. WRN is located on chromosome 8p12 and consists of 34 exons. WRN comprises four domains: a 3'->5' exonuclease domain at the N-terminal, an ATPase domain, an RQC domain that binds to DNA, and an HRDC domain that mediates protein-protein interactions. Among these, the ATPase domain and RQC domain are the core of WRN's helicase function. WRN plays a crucial role in maintaining genomic stability and is involved in DNA replication, transcription, DNA repair, and telomere maintenance. Loss of WRN function leads to cell cycle arrest, DNA damage, mitotic defects, chromosome fragmentation, and apoptosis.
The protein domains and biological functions of WRN [1]
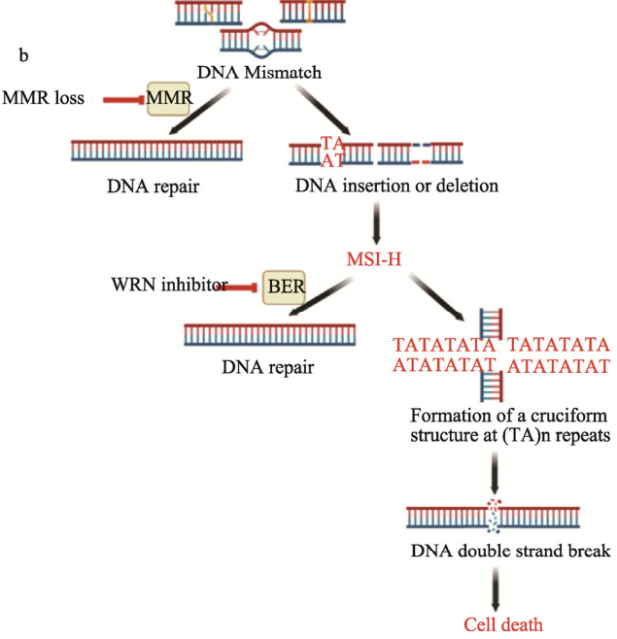
Microsatellites, also known as short tandem repeats (STRs) or simple sequence repeats (SSRs), consist of repeated sequences of 1-6 nucleotides and account for approximately 3% of the genome. The DNA mismatch repair (MMR) system, a highly conserved DNA repair mechanism in cellular evolution that is crucial for maintaining genomic integrity and stability, is widely present in eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Due to the defective MMR system in tumor cells, the genome is prone to insertion or deletion mutations of repeated sequences, leading to the accumulation of replication errors in microsatellite sequences and thus the development of microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) status.
MSI-H is a relatively unique feature of tumor cells, which can further destabilize the genome and drive tumor cell mutations, thereby promoting the initiation and progression of malignant tumors. It is recognized as one of the important carcinogenic pathways. MSI-H is prevalent in various cancers, such as endometrial cancer, gastric cancer, and colorectal cancer, with a prevalence of approximately 11-27%. Patients with MSI-H often respond poorly to traditional chemotherapeutic drugs. Despite the availability of immunotherapy, there remains an unmet clinical need for new drugs.
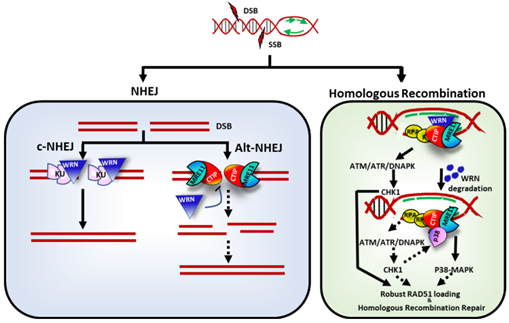
Studies have shown that knockout of the WRN gene or depletion of the WRN protein in MSI-H tumor cells induces a significant synthetic lethal effect, resulting in cell death. This synthetic lethal effect is not dependent on the activity of any other RecQ helicase, but is specifically dependent on WRN, which makes WRN an ideal therapeutic target in MSI-H tumors. Currently, several WRN inhibitors have already entered the early stages of clinical development. Many MNCs, such as Novartis, Bayer, and GSK, have prioritized the development of drugs targeting WRN, with the relevant molecules currently in Phase I/II clinical trials. This fully validates the value of the WRN target.
The IND approval of PH027-1 has significantly narrowed the gap in the clinical development of this target between domestic biopharmaceutical companies and MNCs, demonstrating Puhe Biopharma's competitiveness in global hot drug targets.
The synthetic lethal relationship between WRN and MSI-H [2]
PH027-1 has shown a significant synthetic lethal effect with MSI-H in preclinical data, with strong selectivity for MSI-H cells, indicating the clinical safety potential of this drug. Besides, PH027-1 has also displayed favorable efficacy and safety in animal models.
PH027-1 may also be used in a range of cancers such as gastrointestinal tumors and endometrial cancer, providing new therapeutic options for patients with MSI-H. In addition, this molecule can also be combined with immunotherapy and chemotherapy, further enhancing its therapeutic efficacy and prolonging the survival period of patients with MSI-H. The clinical trial of PH027-1 is also being actively advanced.
About Puhe BioPharma
Suzhou Puhe BioPharma Co., Ltd. is a biotechnology company dedicated to the research and development of innovative small-molecule precision therapeutics. Adhering to the strategy of addressing differential clinical needs, Puhe focuses on cancers with high incidence and mortality rates as well as other chronic diseases. By leveraging scientific and industrial expertise, Puhe combines various advanced technologies such as the next-generation kinase inhibitors, synthetic lethality, PROTACs, and molecular glues to address complex medical challenges. For more information, please visit www.puhebiopharma.com.
References
Gupta P, Majumdar A G, Patro B S. Enigmatic role of WRN-RECQL helicase in DNA repair and its implications in cancer[J]. J. Transl. Genet. Genom, 2022, 6: 147-156.
Van Wietmarschen N, Nathan W J, Nussenzweig A. The WRN helicase: Resolving a new target in microsatellite unstable cancers[J]. Curr Opin Genet Dev, 2021(71): 34-38.